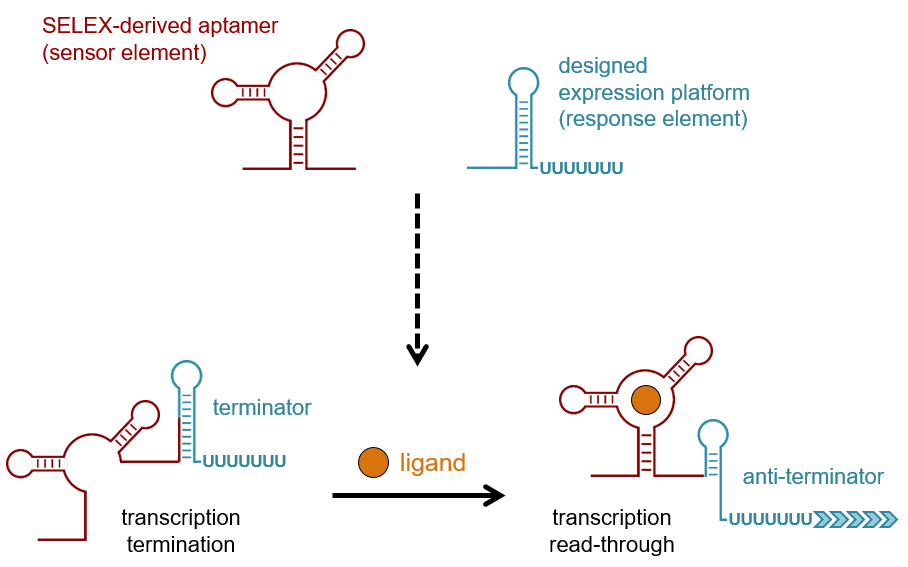
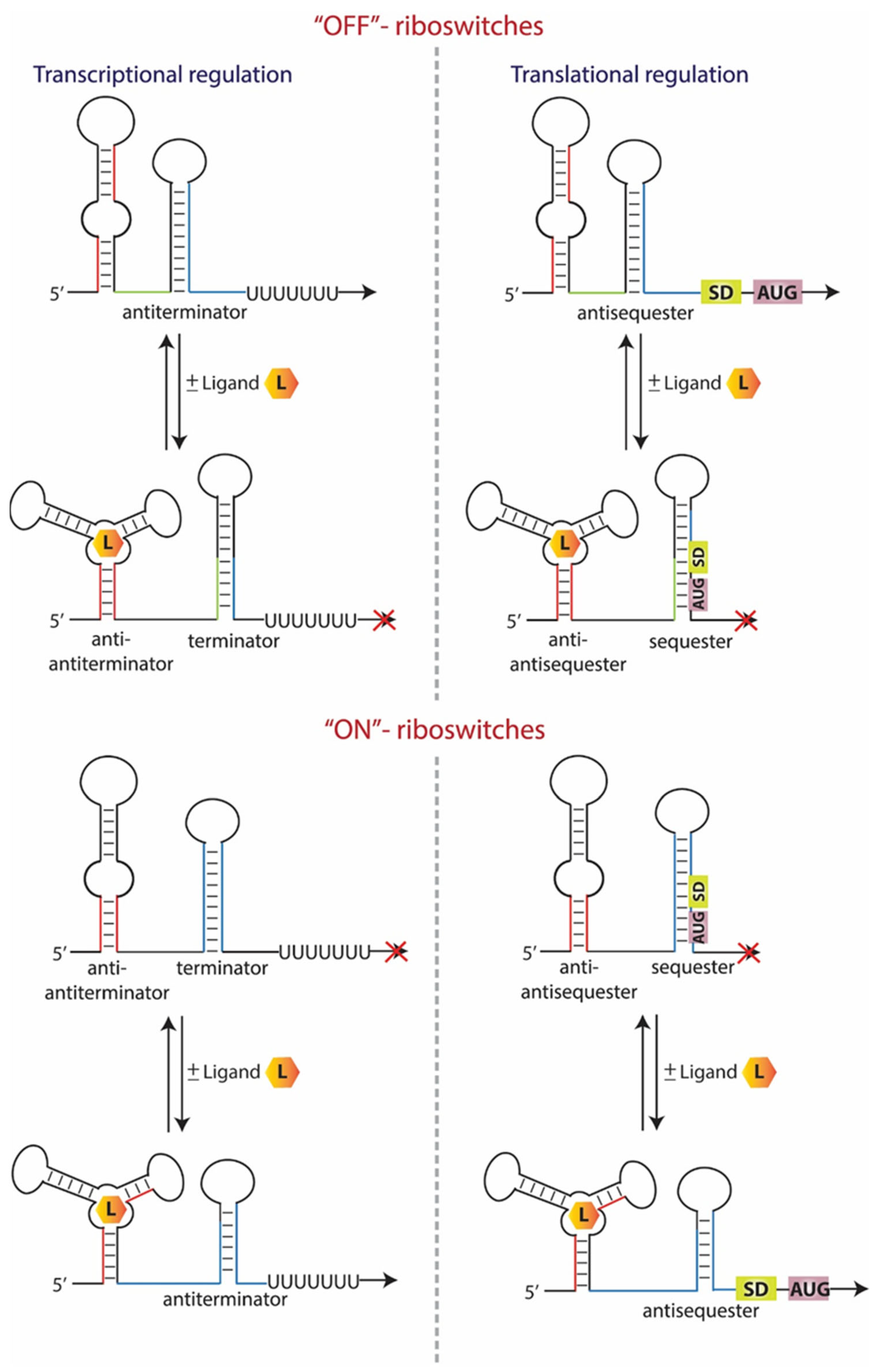
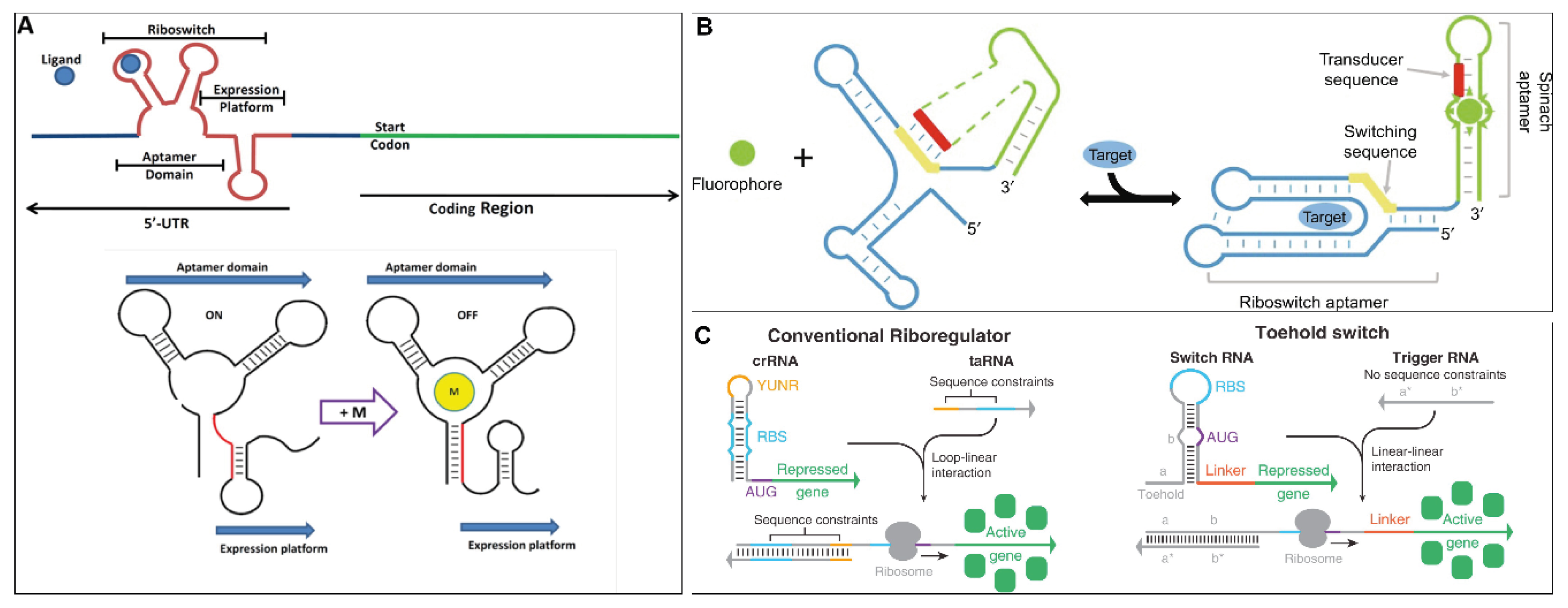
What Are Riboswitches - A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands.
Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands.
A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker.
Universität Leipzig Synthetic Biology
These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues.
Riboswitches Structures and Mechanisms
A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker.
Antibiotics Free FullText A RiboswitchDriven Era of New
Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands. A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues.
Riboswitches DNAdots by miniPCR
A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker.
Riboswitches Definition, Structure, Mechanism and Applications
A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands.
Flipping Riboswitches Cell
Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands.
How molecular riboswitches work in bacteria
A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker.
TeamExeter/RNA Riboswitches
A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands.
Discovering riboswitches the past and the future Trends in
A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands. Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker.
IJMS Free FullText Developments of Riboswitches and Toehold
Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. These regulatory elements are known as riboswitches and are defined as mrna elements that bind metabolites or metal ions as ligands. A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues.
These Regulatory Elements Are Known As Riboswitches And Are Defined As Mrna Elements That Bind Metabolites Or Metal Ions As Ligands.
Riboswitches are structured noncoding rna domains that selectively bind metabolites and control gene expression (mandal and breaker. A critical feature of the hypothesized rna world would have been the ability to control chemical processes in response to environmental cues.