How To Find Energy Dissipated How To Find - Processes in which some amount of mechanical energy disappears (that is, it cannot be found anywhere anymore as either macroscopic. \[ e = \frac{ted}{t} \] where: P = r\cdot i^2 p =. There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. The first one requires you to know resistance and current: When current flows through a resistor, electricity is falling through a potential difference. When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. \(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules. An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit of time a system can dissipate. The higher the dissipation rate, the.
When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. When current flows through a resistor, electricity is falling through a potential difference. \[ e = \frac{ted}{t} \] where: The higher the dissipation rate, the. The first one requires you to know resistance and current: Processes in which some amount of mechanical energy disappears (that is, it cannot be found anywhere anymore as either macroscopic. There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. P = r\cdot i^2 p =. \(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules. To calculate the energy dissipation rate, use the formula:
\(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules. The first one requires you to know resistance and current: P = r\cdot i^2 p =. When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. When current flows through a resistor, electricity is falling through a potential difference. To calculate the energy dissipation rate, use the formula: Processes in which some amount of mechanical energy disappears (that is, it cannot be found anywhere anymore as either macroscopic. There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. The higher the dissipation rate, the. An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit of time a system can dissipate.
Power Dissipated By Resistor Equation Tessshebaylo
There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. The first one requires you to know resistance and current: P = r\cdot i^2 p =. To calculate the energy dissipation rate, use the formula: An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit of time a system can dissipate.
Question Video Recalling the Formula for Dissipated Energy Nagwa
The higher the dissipation rate, the. Processes in which some amount of mechanical energy disappears (that is, it cannot be found anywhere anymore as either macroscopic. P = r\cdot i^2 p =. When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. \(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules.
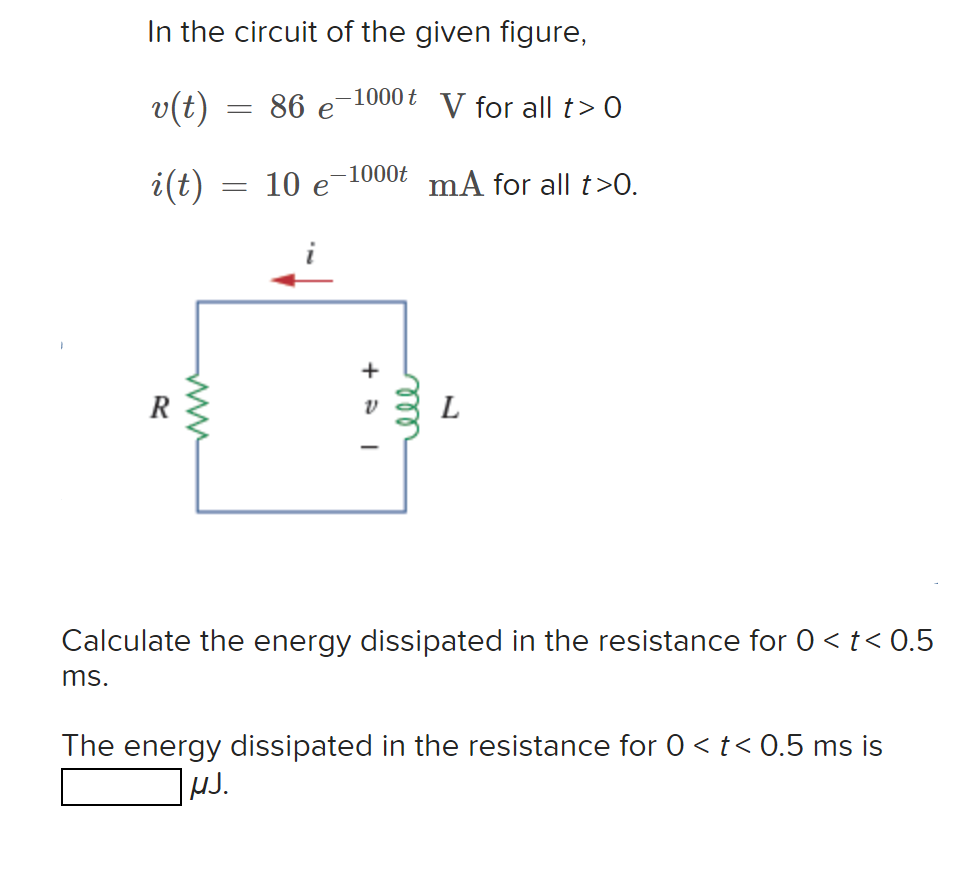
Solved In the circuit of the given figure, 1000 t v(t) = 86
P = r\cdot i^2 p =. There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. \(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules. An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit of time a system can dissipate.
Find the Total Power Dissipated in the Circuit LandonminCarpenter
There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. P = r\cdot i^2 p =. When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. To calculate the energy dissipation rate, use the formula: An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit of time a system can dissipate.
How to Find Energy Dissipated by a Resistor A Comprehensive Guide
\[ e = \frac{ted}{t} \] where: When current flows through a resistor, electricity is falling through a potential difference. The higher the dissipation rate, the. To calculate the energy dissipation rate, use the formula: An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit of time a system can dissipate.
Question Video Finding the Rate of Energy Dissipation Nagwa
Processes in which some amount of mechanical energy disappears (that is, it cannot be found anywhere anymore as either macroscopic. To calculate the energy dissipation rate, use the formula: There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. \[ e = \frac{ted}{t} \] where: \(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules.
How To Find Dissipated Power in a Resistor Circuit Analysis Solved
Processes in which some amount of mechanical energy disappears (that is, it cannot be found anywhere anymore as either macroscopic. The higher the dissipation rate, the. When current flows through a resistor, electricity is falling through a potential difference. When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit.
Energy Dissipated by Frictional Forces as an Object with Potential
The higher the dissipation rate, the. Processes in which some amount of mechanical energy disappears (that is, it cannot be found anywhere anymore as either macroscopic. P = r\cdot i^2 p =. When current flows through a resistor, electricity is falling through a potential difference. \(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules.
¿Cómo calculas la disipación de potencia de una resistencia?
When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. To calculate the energy dissipation rate, use the formula: \(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules. There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. \[ e = \frac{ted}{t} \] where:
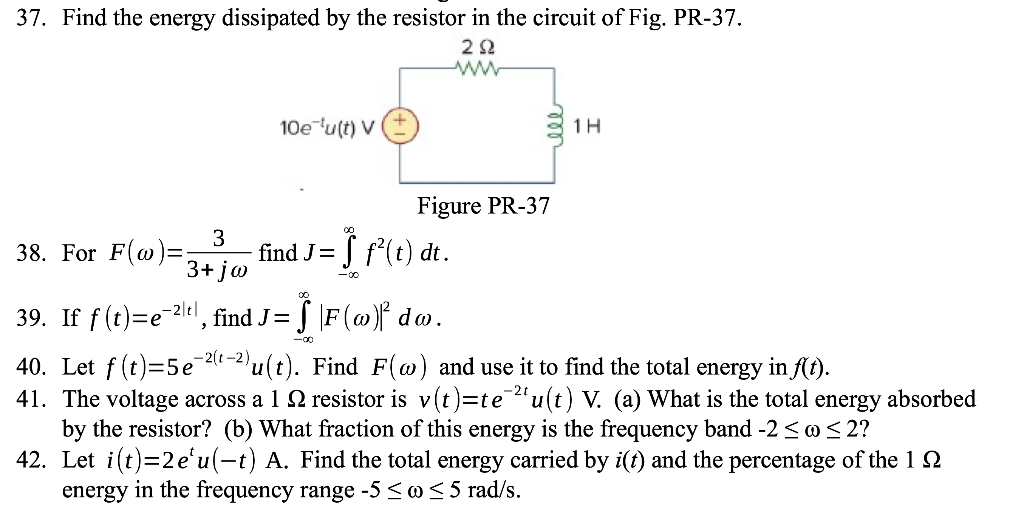
Solved 37. Find the energy dissipated by the resistor in the
When current flows through a resistor, electricity is falling through a potential difference. The first one requires you to know resistance and current: \[ e = \frac{ted}{t} \] where: An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit of time a system can dissipate. The higher the dissipation rate, the.
The Higher The Dissipation Rate, The.
\(e\) is the energy dissipation rate in joules. Processes in which some amount of mechanical energy disappears (that is, it cannot be found anywhere anymore as either macroscopic. When a coulomb drops through a volt, it loses potential. The first one requires you to know resistance and current:
\[ E = \Frac{Ted}{T} \] Where:
An energy dissipation rate is the amount of energy per unit of time a system can dissipate. To calculate the energy dissipation rate, use the formula: There are two possible formulas for power dissipation. P = r\cdot i^2 p =.