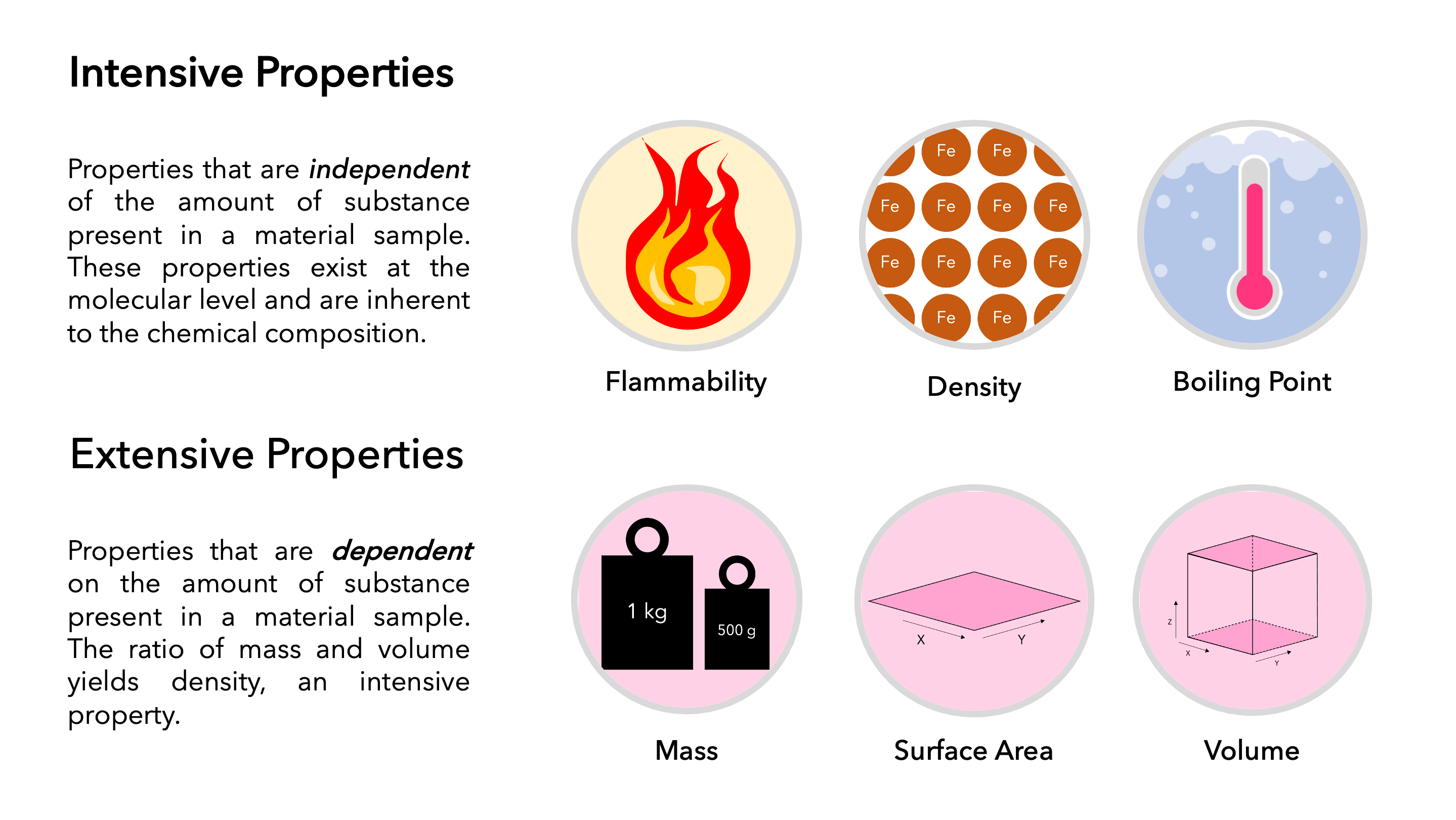
Extensive Vs Intensive Properties - The ratio of two extensive properties of the same object or system is an intensive property. Mass and volume are examples of extensive properties. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties, is. Extensive properties vary with the amount of the substance and include mass, weight, and volume. An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. An intensive property is a property of matter that. Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties. Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter in a substance.
An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. Extensive properties vary with the amount of the substance and include mass, weight, and volume. Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. An intensive property is a property of matter that. For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties, is. Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter in a substance. Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of physical properties of matter. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; The ratio of two extensive properties of the same object or system is an intensive property. The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties.
Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of physical properties of matter. An intensive property is a property of matter that. Extensive properties vary with the amount of the substance and include mass, weight, and volume. The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties. Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter in a substance. Mass and volume are examples of extensive properties. Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties, is.
Extensive Properties Vs Intensive Properties
For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties, is. The ratio of two extensive properties of the same object or system is an intensive property. An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter in a.
Intensive vs. Extensive Property What's the Difference? • 7ESL
Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter in a substance. For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties, is. Mass and volume are examples of extensive properties. An extensive property is a property that depends on the.
Difference Between Intensive Property and Extensive Property
For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties, is. Extensive properties vary with the amount of the substance and include mass, weight, and volume. The ratio of two extensive properties of the same object or system is an intensive property. An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter.
PPT Properties & Changes in Matter Extensive vs. Intensive Physical
Mass and volume are examples of extensive properties. Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of physical properties of matter. The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties. Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a.
Extensive and Intensive Properties Study Guide Inspirit
For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties, is. Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter in a substance. The ratio of two extensive properties of the.
Intensive vs. Extensive Property What's the Difference? • 7ESL
An intensive property is a property of matter that. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of physical properties of matter. For example, the ratio of an object's mass and.
Difference Between Intensive and Extensive Properties Definition
Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of physical properties of matter. An intensive property is a property of matter that. For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties,.
The Difference Between Intensive and Extensive Properties
Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of physical properties of matter. The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties. Extensive properties vary with the amount of the substance and include mass, weight, and volume. Mass and volume are examples of extensive properties. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount.
Intensive and extensive properties YouTube
Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. An intensive property is a property of matter that. The ratio of two extensive properties of the same object or system is an intensive property. Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of.
Extensive vs. Intensive Properties — Overview & Examples Expii
Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter in a substance. The two types of physical properties of matter are intensive properties and extensive properties. Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of physical properties of matter. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; The ratio of two extensive properties of.
The Two Types Of Physical Properties Of Matter Are Intensive Properties And Extensive Properties.
Mass and volume are examples of extensive properties. For example, the ratio of an object's mass and volume, which are two extensive properties, is. An intensive property is a property of matter that. The ratio of two extensive properties of the same object or system is an intensive property.
An Extensive Property Is A Property That Depends On The Amount Of Matter In A Sample.
Intensive properties do not depend on the amount of matter in a substance. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; Intensive properties do not depend on the quantity of matter. Extensive and intensive properties are the two types of physical properties of matter.



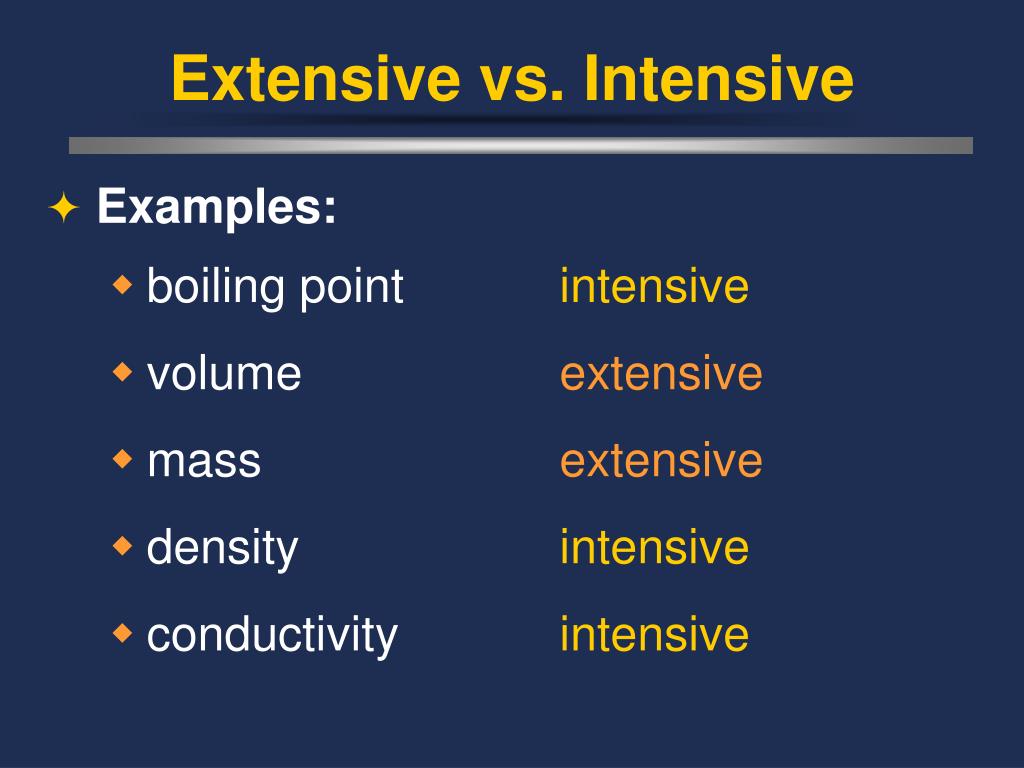



/intensive-vs-extensive-properties-604133-v3-5b55fb394cedfd0037117796.png)