Bias Definition In Math - Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias can skew the results of. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data.
A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias can skew the results of.
Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias can skew the results of. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter.
What Is Bias Meaning, Concept, Types, And Action Steps
Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. Bias can skew the results of. Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set.
Understanding ascertainment bias in biomedical research Implications
A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. Bias can skew the results of. Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to.
15 Statistical Bias Examples (2024)
Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data. Bias can skew the.
Understanding unconscious bias in the workplace Definitions, examples
Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data. Bias can skew the results of. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a.
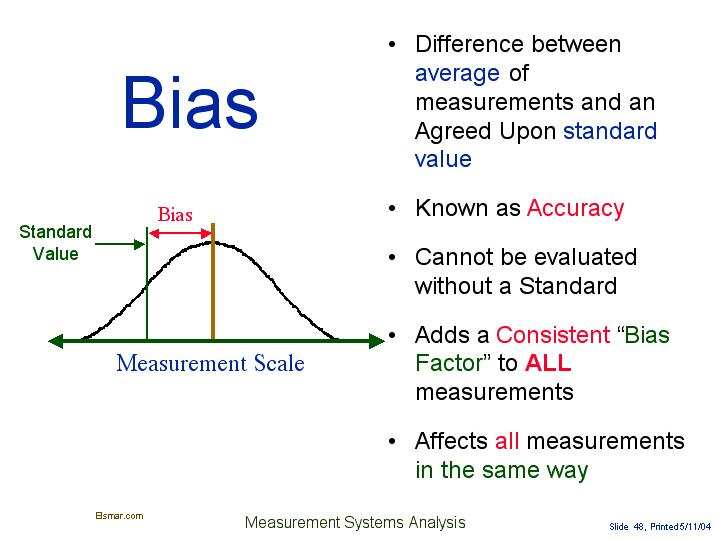
Bias
Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. Bias can skew the results of. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set.
WHAT IS BIAS YouTube
Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data. Bias can skew the results of. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a.
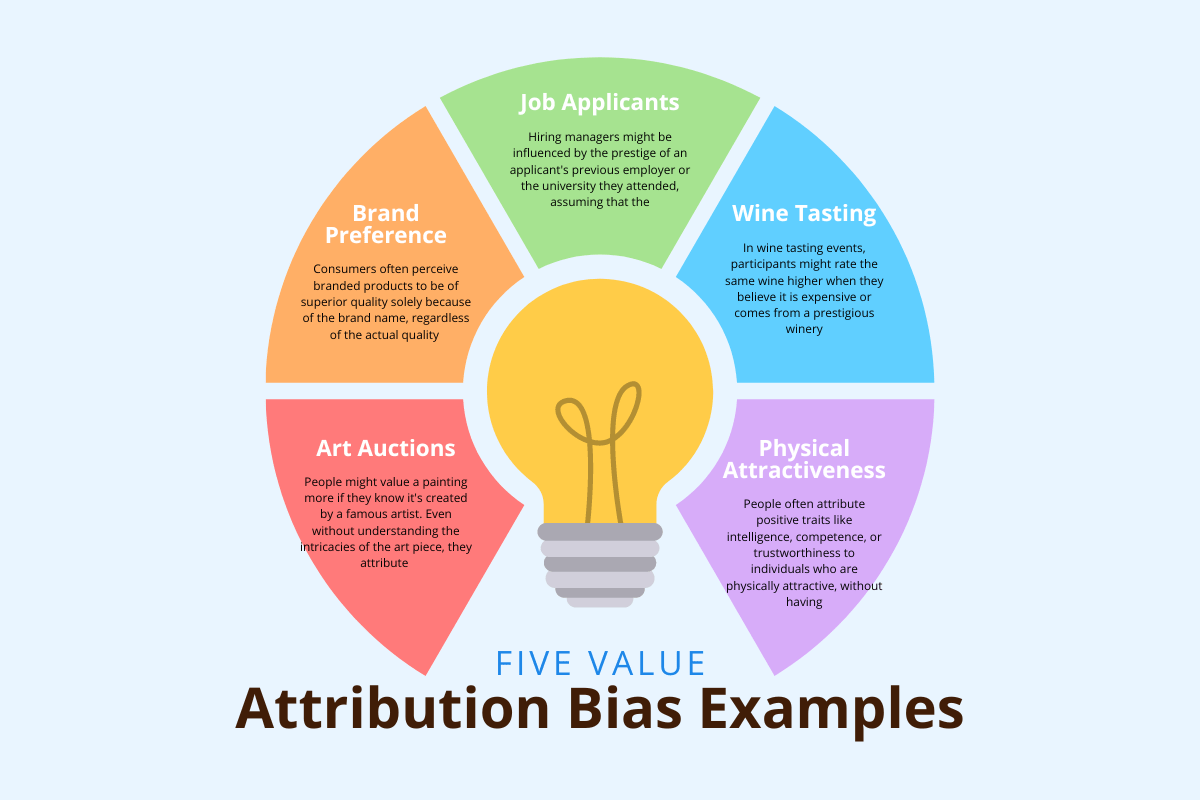
Value Attribution Bias A Definitive Guide Explained with 5 Examples
Bias can skew the results of. Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set.
Best biased vs unbiased questions
Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data. Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias can skew the.
What is Response Bias? + [Examples & Ways to Minimize It]
Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias can skew the results of. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set.
What Does Draw Bias Mean
Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter. A bias is the deliberate or involuntary favouring of one class or outcome over other potential groups or outcomes in the chosen set of data. Bias can skew the.
A Bias Is The Deliberate Or Involuntary Favouring Of One Class Or Outcome Over Other Potential Groups Or Outcomes In The Chosen Set Of Data.
Bias can skew the results of. Bias refers to a systematic error that skews results or interpretations in a particular direction, often leading to misleading conclusions. Bias is the tendency to overestimate or underestimate a population parameter.






![What is Response Bias? + [Examples & Ways to Minimize It]](https://www.driveresearch.com/media/5169/example-of-dissent-and-acquiescence-bias.png)
