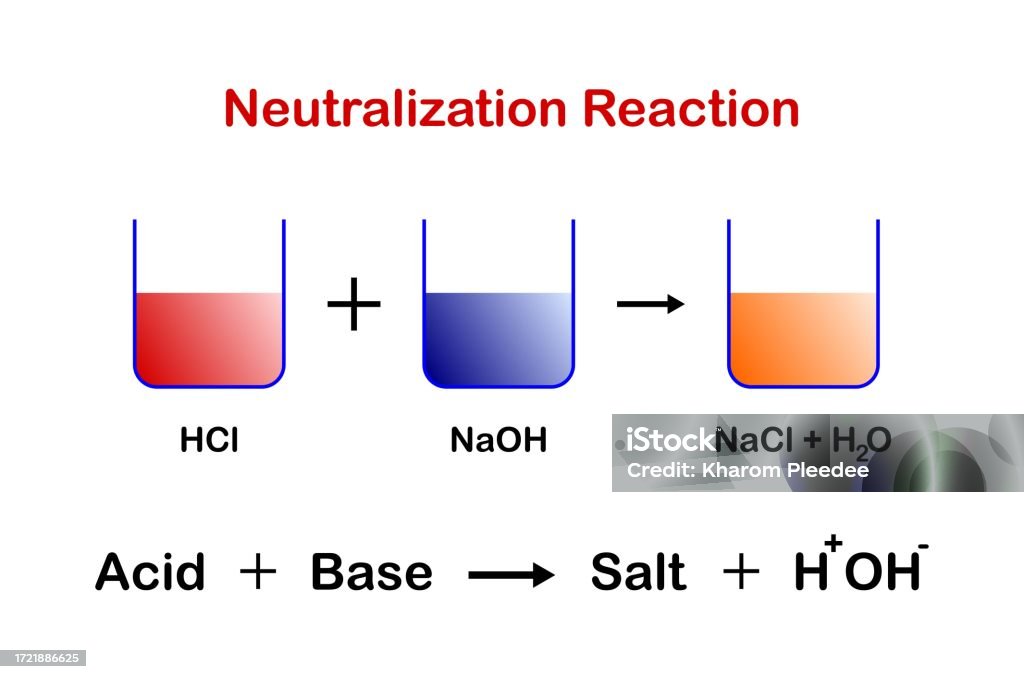
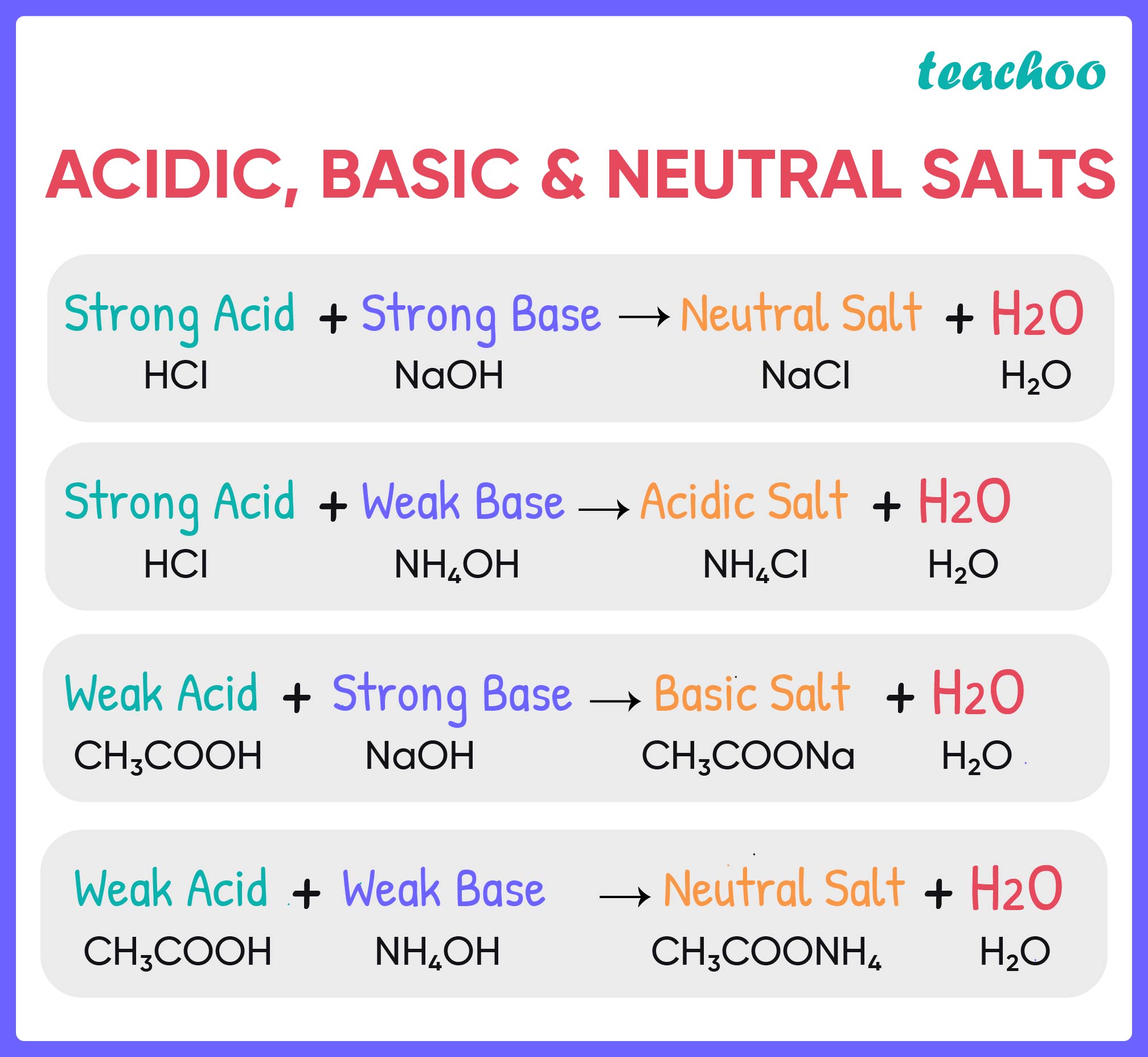
Acids React With Bases To Form Salt And Water - In a neutralisation reaction, an acid and a base combine to form a. Acids react with bases to form a salt and water. Salt solutions do not always. The acid and base have neutralized each other, and the acidic and basic properties are no longer present. Acid + base → salt + water. When an acid reacts with a base, we get salt and water as products. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Sulfuric acid + copper (ii) oxide → copper (ii) sulfate + water. Acids react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form salts and water.
The acid and base have neutralized each other, and the acidic and basic properties are no longer present. Acid + base → salt + water. Hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium. Acids react with bases to form a salt and water. Sulfuric acid + copper (ii) oxide → copper (ii) sulfate + water. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Acids react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form salts and water. Salt solutions do not always. When an acid reacts with a base, we get salt and water as products. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and.
In a neutralisation reaction, an acid and a base combine to form a. Acid + base → salt + water. Sulfuric acid + copper (ii) oxide → copper (ii) sulfate + water. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium. When an acid reacts with a base, we get salt and water as products. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and. Acids react with bases to form a salt and water. Salt solutions do not always. Acids react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form salts and water.
Acids and Bases Science with Mrs Beggs
Salt solutions do not always. Hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium. Acids react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form salts and water. Acid + base → salt + water. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and.
Acids React With Bases To Produce Salt And Water Stock Illustration
When an acid reacts with a base, we get salt and water as products. The acid and base have neutralized each other, and the acidic and basic properties are no longer present. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and. In a neutralisation reaction, an acid and a base combine to form a. Acid.
Acid Base Reaction Examples
Salt solutions do not always. Acids react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form salts and water. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Acids react with bases to form a salt and water. In a neutralisation reaction, an acid and a base combine to form a.
A Level Chemistry Revision Physical Chemistry Acids And Bases
Acids react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form salts and water. Acids react with bases to form a salt and water. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and. Sulfuric acid + copper (ii) oxide → copper.
Acids, Bases and Salts class 7 worksheet witknowlearn Acids bases
When an acid reacts with a base, we get salt and water as products. In a neutralisation reaction, an acid and a base combine to form a. Acid + base → salt + water. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Salt solutions do not always.
Acids, Bases, And Salts Definition, Types, Properties, And, 51 OFF
Sulfuric acid + copper (ii) oxide → copper (ii) sulfate + water. Acids react with bases to form a salt and water. Acid + base → salt + water. In a neutralisation reaction, an acid and a base combine to form a. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and.
Salts and it's Properties (with Examples) Acids, Bases and Salt
Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and. Acids react with bases to form a salt and water. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Salt solutions do not always. Acid + base → salt + water.
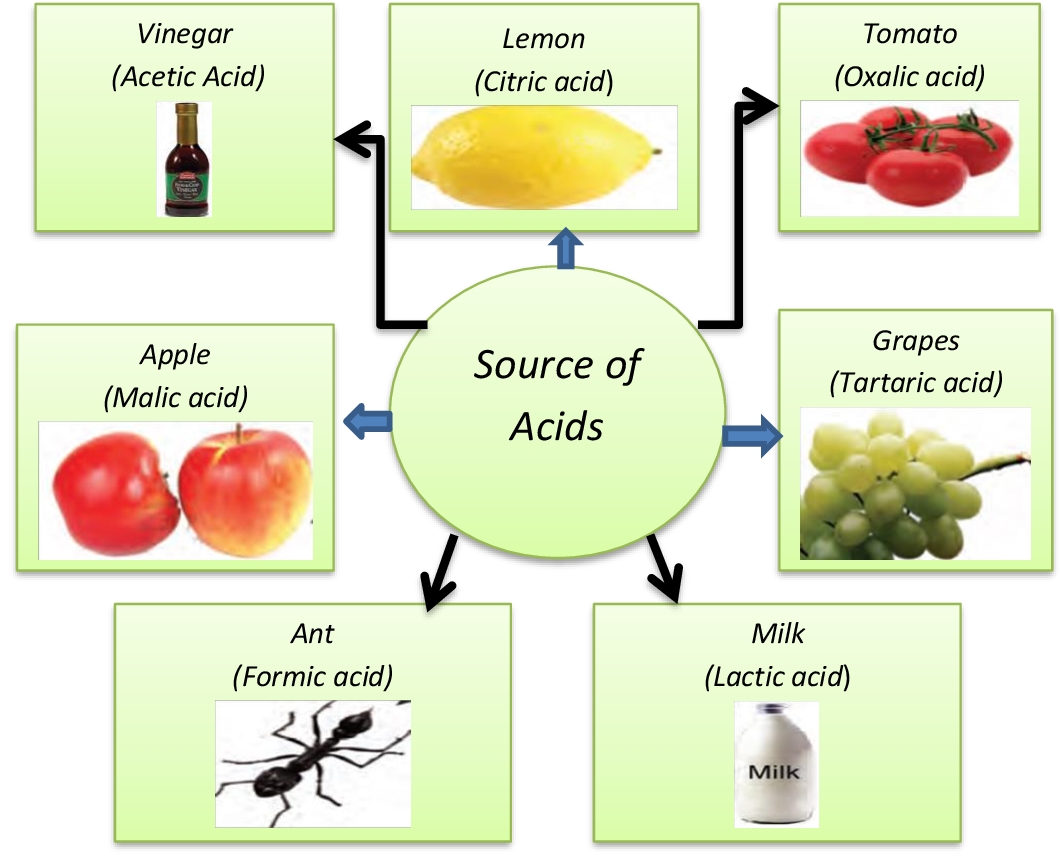
Acids and it's Properties Definition [with Flowchart and Examples]
When an acid reacts with a base, we get salt and water as products. The acid and base have neutralized each other, and the acidic and basic properties are no longer present. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and. Sulfuric acid + copper (ii) oxide → copper (ii) sulfate + water. Acids react.
Lesson Plan of Properties and Uses of Acids (Acids, Alkalies and Salts
The acid and base have neutralized each other, and the acidic and basic properties are no longer present. Salt solutions do not always. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and. Sulfuric acid + copper (ii) oxide → copper.
Acids react with bases to form salt and water. This reaction is known as
Acids react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form salts and water. In a neutralisation reaction, an acid and a base combine to form a. Acid + base → salt + water. Sulfuric acid + copper (ii) oxide → copper (ii) sulfate + water. Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and.
Salt Solutions Do Not Always.
In a neutralisation reaction, an acid and a base combine to form a. The acid and base have neutralized each other, and the acidic and basic properties are no longer present. When an acid reacts with a base, we get salt and water as products. When an acid and a base are combined, water and a salt are the products.
Sulfuric Acid + Copper (Ii) Oxide → Copper (Ii) Sulfate + Water.
Salts are ionic compounds containing a positive ion other than h+ h + and. Acid + base → salt + water. Acids react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form salts and water. Hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium.




.png)
![Acids and it's Properties Definition [with Flowchart and Examples]](https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/28568581-671c-4933-be3c-3b6bced35321/some-properties-of-acids-teachoo.jpg)